基于Java的Web 应用程序是 servlet、JSP 页面、静态页面、类和其他资源的集合,它们可以用标准方式打包,并运行在来自多个供应商的多个容器。Web 应用程序存在于结构化层次结构的目录中,该层次结构是由 Java Servlet 规范定义的。Web 应用程序的根目录包含直接存储或存储在子文件夹中的所有公共资源,比如图像、HTML 页面等。构成:Web应用由Web组件(一组Java类库)、html文件,静态资源文件(如图像)、帮助类和库组成。
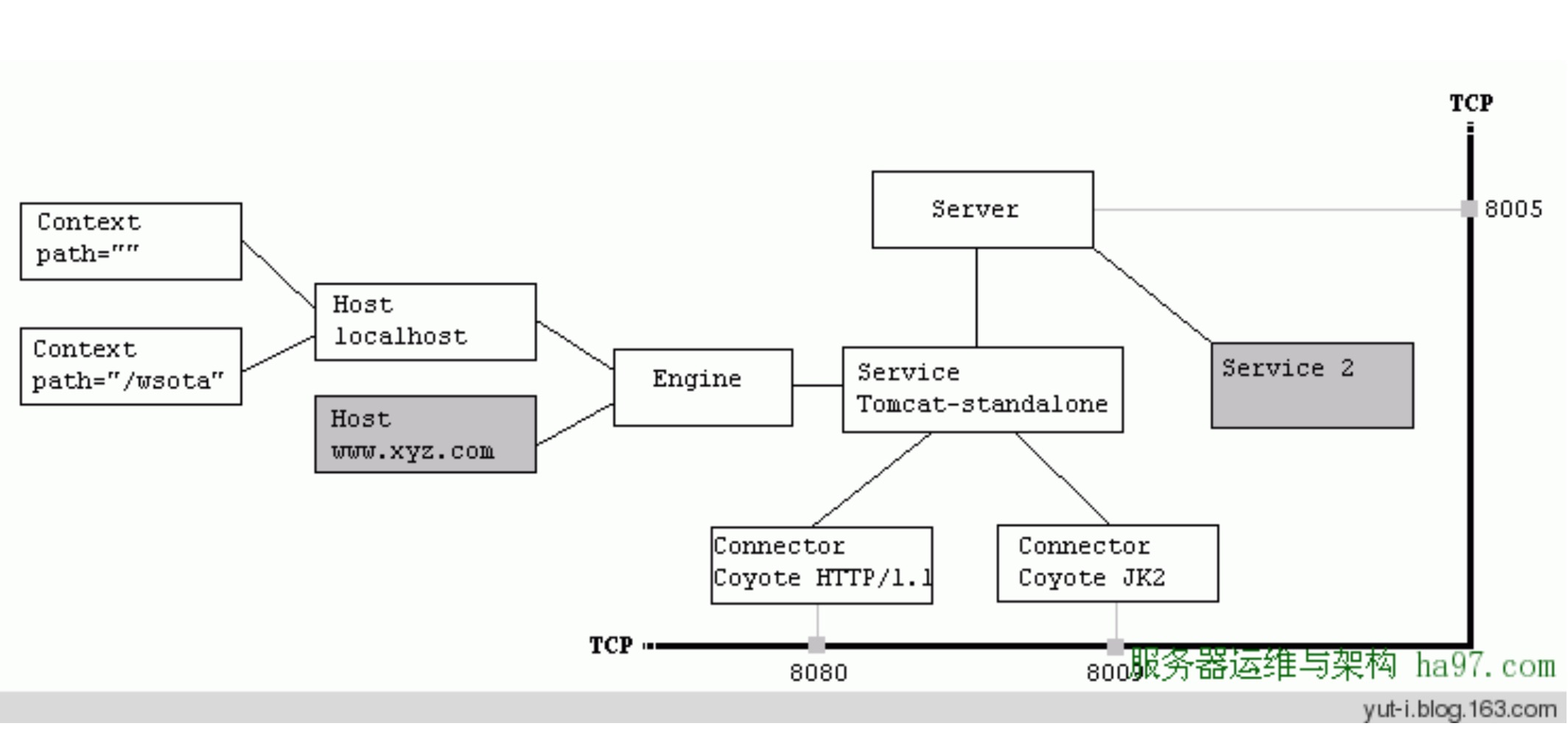
1 – Tomcat Server的组成部分 1.1 – Server A Server element represents the entire Catalina servlet container. (Singleton)
1.2 – Service A Service element represents the combination of one or more Connector components that share a single Engine
Service是这样一个集合:它由一个或者多个Connector组成,以及一个Engine,负责处理所有Connector所获得的客户请求
1.3 – Connector 一个Connector将在某个指定端口上侦听客户请求,并将获得的请求交给Engine来处理,从Engine处获得回应并返回客户
TOMCAT有两个典型的Connector,一个直接侦听来自browser的http请求,一个侦听来自其它WebServer的请求
Coyote Http/1.1 Connector 在端口8080处侦听来自客户browser的http请求
Coyote JK2 Connector 在端口8009处侦听来自其它WebServer(Apache)的servlet/jsp代理请求
1.4 – Engine The Engine element represents the entire request processing machinery associated with a particular Service
Engine下可以配置多个虚拟主机Virtual Host,每个虚拟主机都有一个域名
Engine有一个默认虚拟主机,当请求无法匹配到任何一个Host上的时候,将交给该默认Host来处理
1.5 – Host 代表一个Virtual Host,虚拟主机,每个虚拟主机和某个网络域名Domain Name相匹配
每个虚拟主机下都可以部署(deploy)一个或者多个Web App,每个Web App对应于一个Context,有一个Context path
当Host获得一个请求时,将把该请求匹配到某个Context上,然后把该请求交给该Context来处理
匹配的方法是“最长匹配”,所以一个path==””的Context将成为该Host的默认Context
所有无法和其它Context的路径名匹配的请求都将最终和该默认Context匹配
1.6 – Context 一个Context对应于一个Web Application,一个Web Application由一个或者多个Servlet组成
Context在创建的时候将根据配置文件$CATALINA_HOME/conf/web.xml和$WEBAPP_HOME/WEB-INF/web.xml载入Servlet类
当Context获得请求时,将在自己的映射表(mapping table)中寻找相匹配的Servlet类
如果找到,则执行该类,获得请求的回应,并返回
2 – Tomcat Server的结构图
3 – 配置文件$CATALINA_HOME/conf/server.xml的说明 该文件描述了如何启动Tomcat Server
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 <Server port ="8005" shutdown ="SHUTDOWN" debug ="0" > <Listener className ="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.ServerLifecycleListener" debug ="0" /> <Listener className ="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener" debug ="0" /> <GlobalNamingResources > ... ... ... ... </GlobalNamingResources > <Service name ="Tomcat-Standalone" > <Connector className ="org.apache.coyote.tomcat4.CoyoteConnector" port ="8080" minProcessors ="5" maxProcessors ="75" acceptCount ="100" enableLookups ="true" redirectPort ="8443" debug ="0" connectionTimeout ="20000" useURIValidationHack ="false" disableUploadTimeout ="true" /> <Engine name ="Standalone" defaultHost ="localhost" debug ="0" > <Logger className ="org.apache.catalina.logger.FileLogger" ... /> <Realm className ="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm" ... /> <Host name ="localhost" debug ="0" appBase ="webapps" unpackWARs ="true" autoDeploy ="true" > <Logger className ="org.apache.catalina.logger.FileLogger" ... /> <Context path ="" docBase ="mycontext" debug ="0" /> <Context path ="/wsota" docBase ="wsotaProject" debug ="0" /> </Host > </Engine > </Service > </Server >
4 – Context的部署配置文件web.xml的说明 一个Context对应于一个Web App,每个Web App是由一个或者多个servlet组成的
当一个Web App被初始化的时候,它将用自己的ClassLoader对象载入“部署配置文件web.xml”中定义的每个servlet类
它首先载入在$CATALINA_HOME/conf/web.xml中部署的servlet类
然后载入在自己的Web App根目录下的WEB-INF/web.xml中部署的servlet类
每个被载入的servlet类都有一个名字,且被填入该Context的映射表(mapping table)中,和某种URL PATTERN对应
当该Context获得请求时,将查询mapping table,找到被请求的servlet,并执行以获得请求回应
分析一下所有的Context共享的web.xml文件,在其中定义的servlet被所有的Web App载入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 <web-app > <servlet > <servlet-name > default</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.apache.catalina.servlets.DefaultServlet </servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > debug</param-name > <param-value > 0</param-value > </init-param > <init-param > <param-name > listings</param-name > <param-value > true</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup > </servlet > <servlet > <servlet-name > invoker</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.apache.catalina.servlets.InvokerServlet </servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > debug</param-name > <param-value > 0</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 2</load-on-startup > </servlet > <servlet > <servlet-name > jsp</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > logVerbosityLevel</param-name > <param-value > WARNING</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 3</load-on-startup > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > default</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > invoker</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /servlet/*</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > jsp</servlet-name > <url-pattern > *.jsp</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > ... ... ... ... </web-app >
5 – Tomcat Server处理一个http请求的过程 假设来自客户的请求为:
http://localhost:8080/wsota/wsota_index.jsp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 1) 请求被发送到本机端口8080,被在那里侦听的Coyote HTTP/1.1 Connector获得 2) Connector把该请求交给它所在的Service的Engine来处理,并等待来自Engine的回应 3) Engine获得请求localhost/wsota/wsota_index.jsp,匹配它所拥有的所有虚拟主机Host 4) Engine匹配到名为localhost的Host(即使匹配不到也把请求交给该Host处理,因为该Host被定义为该Engine的默认主机) 5) localhost Host获得请求/wsota/wsota_index.jsp,匹配它所拥有的所有Context 6) Host匹配到路径为/wsota的Context(如果匹配不到就把该请求交给路径名为”"的Context去处理) 7) path=”/wsota”的Context获得请求/wsota_index.jsp,在它的mapping table中寻找对应的servlet 8) Context匹配到URL PATTERN为*.jsp的servlet,对应于JspServlet类 9) 构造HttpServletRequest对象和HttpServletResponse对象,作为参数调用JspServlet的doGet或doPost方法 10)Context把执行完了之后的HttpServletResponse对象返回给Host 11)Host把HttpServletResponse对象返回给Engine 12)Engine把HttpServletResponse对象返回给Connector 13)Connector把HttpServletResponse对象返回给客户browser
来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/boblogsbo/p/5207205.html
tomcat配置多个虚拟主机 先修改默认端口(8080),http的默认端口是80,我们将8080改成80,这样域名就不用带上端口了
修改conf文件夹下的server.xml文件
添加多个主机(以下三个主机对应三个域名,三个域名对应同一个ip地址)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 <Host appBase ="D:" autoDeploy ="true" name ="wap.test.com" unpackWARs ="true" xmlNamespaceAware ="false" xmlValidation ="false" > <Context docBase ="D:\wap" path ="" reloadable ="true" crossContext ="true" /> </Host > <Host appBase ="D:" autoDeploy ="true" name ="web.test.com" unpackWARs ="true" xmlNamespaceAware ="false" xmlValidation ="false" > <Context docBase ="D:\web" path ="" reloadable ="true" crossContext ="true" /> </Host > <Host appBase ="D:" autoDeploy ="true" name ="manage.test.com" unpackWARs ="true" xmlNamespaceAware ="false" xmlValidation ="false" > <Context docBase ="D:\manage" path ="" reloadable ="true" crossContext ="true" /> </Host >
<host>中的元素:appBase–>项目文件夹的父目录 name–>该主机对应的域名,其他元素自己百度
<context>中的元素:docBase–>对应项目文件夹或者项目的.war包(如果是war包,就需要把unpackWARs设置为true)
path–>访问时如果要带上项目名就添加项目名,不需要(直接域名访问)就为空。
我们在windows中测试:修改C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc下的hosts文件。添加三个模拟的域名1 2 3 127.0.0.1 wap.test.com 127.0.0.1 web.test.com 127.0.0.1 manage.test.com
三个域名对应的是同一个ip地址,即本地的ip地址。
来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/LvLoveYuForever/p/5886788.html